Quite a few people say that Big Data is the new oil, and there is something to that. We can mine data, and sometimes there happens to be a data leak. We can also gather data and use it to create value. By analogy, data management can't be uncontrolled and spontaneous. If handled without care, it might end up being a threat to brand reputation and user safety.
Luckily, you can take care of that by looking into privacy by design. Privacy by design is built on foundational principles that ensure data protection and user trust from the ground up. Wondering what it is and how it works? No worries, our article should help you get the hang of it in no time! Check it out, and start building an honest relationship between your product and the people who use it.


 ## What Is Considered To Be Personal Data?
## What Is Considered To Be Personal Data?
First, we need to establish what personal data is. Its definition is fairly simple. In short, it'’s everything that allows you to identify a person. Such a definition might cause a few obvious examples to come to mind, such as as someone'’s full name and their address, but in reality, it'’s much more than that. In fact, a person can be identified through their IP or their cookie ID. Additionally, sensitive data such as health records and financial information require even more stringent protection measures.
Privacy by Design Meaning
So, what is privacy by design? The privacy by design definition states that it’s an approach to systems engineering that was initially developed by Ann Cavoukian, the former Information and Privacy Commissioner of Ontario. It was developed in 1995 and published in 2009. At its core, it’s about being mindful of personal data protection and privacy throughout the entirety of the engineering process, not just a part of it. Privacy by design principles should be integrated throughout the entire data lifecycle, from initial collection to final disposal.

Core Principles of Privacy by Design
According to Ann, professionals who are interested in privacy by design should follow several key rules. Most importantly, one should prioritize proactivity and functionality, as well as ensure that customer data is safe throughout the entire product lifecycle. In addition, Ann puts an emphasis on transparency. She viewed it as the cornerstone of building trust. Integrating privacy into every business practice ensures that data protection is a fundamental aspect of your operations. In the following section, we will elaborate on each of the principles Ann outlined in her publication.
Proactive, Not Reactive
It’s important that you prevent data misuse before it actually happens. In practice, it means looking for vulnerabilities in your processing system that could lead to a data breach. Whether it be a specific feature, an internal system, or a third-party contractor that you are planning on working with, you need to figure out how using it might compromise user privacy.
Having identified potential problems, come up with reliable ways to prevent the said problems from occurring. In addition, you might want to prepare procedures that should be used in case a data breach does occur.
Treat Privacy As the Default Setting
Users shouldn't have to worry about going through the settings of a website or an application in order to make sure that their data is secure. Instead, the highest level of data security should be ensured by default, regardless of whether the user interacts with the settings.
Integrate Privacy Into Product Design
Privacy-related matters aren't to be treated as an afterthought. They shouldn't be an extra feature that you just tack on at the end of a project. Instead, they should be integrated into product design from the very beginning of the design process.
Ensure Full Functionality, No Trade-Offs
If you're designing something, you should make sure that data security features don't detract from things like user experience or existing security protocols. In fact, they should work seamlessly with every single design element.
Guarantee End-to-End Security
Remember to care for data subject information throughout the product lifecycle. Start with the moment a user signs up. Do they know what data they are sharing with you? Can they choose not to do so? Later on, they should find it easy to go back to these settings and change them.
Next, come up with ways to get rid of data that you no longer need. Once that is taken care of, ensure that users can ask you to delete their data from your systems. Aside from their data, they should be able to delete their accounts in their entirety. Sure, it's natural that you don't want them to leave, but keeping them in your system against their will is just going to result in frustration.
Prioritize Visibility and Transparency
Without transparency, you won't be able to make your users trust you. If you want to build customer relationships based on trust, you should treat transparency as a top priority. In other words, you should make sure that they know what you're doing with their data.
Sharing detailed documentation about how your company handles data privacy isn't enough. After all, it's probably filled with jargon and complicated phrasing that an average user simply won't understand. As an alternative, you could add a section about data privacy to your website and ensure that it's written in plain language. That way, you will be able to ensure that both you and your users are on the same page regarding this very important topic.
Be User-Centric
You should always have the user's best interest in mind. So, make sure that they are always in control of their data. Better yet, hear them out and seek their engagement in the data management process. By doing so, you show them that you respect them, which is bound to have a positive impact on your users' perception of your brand.
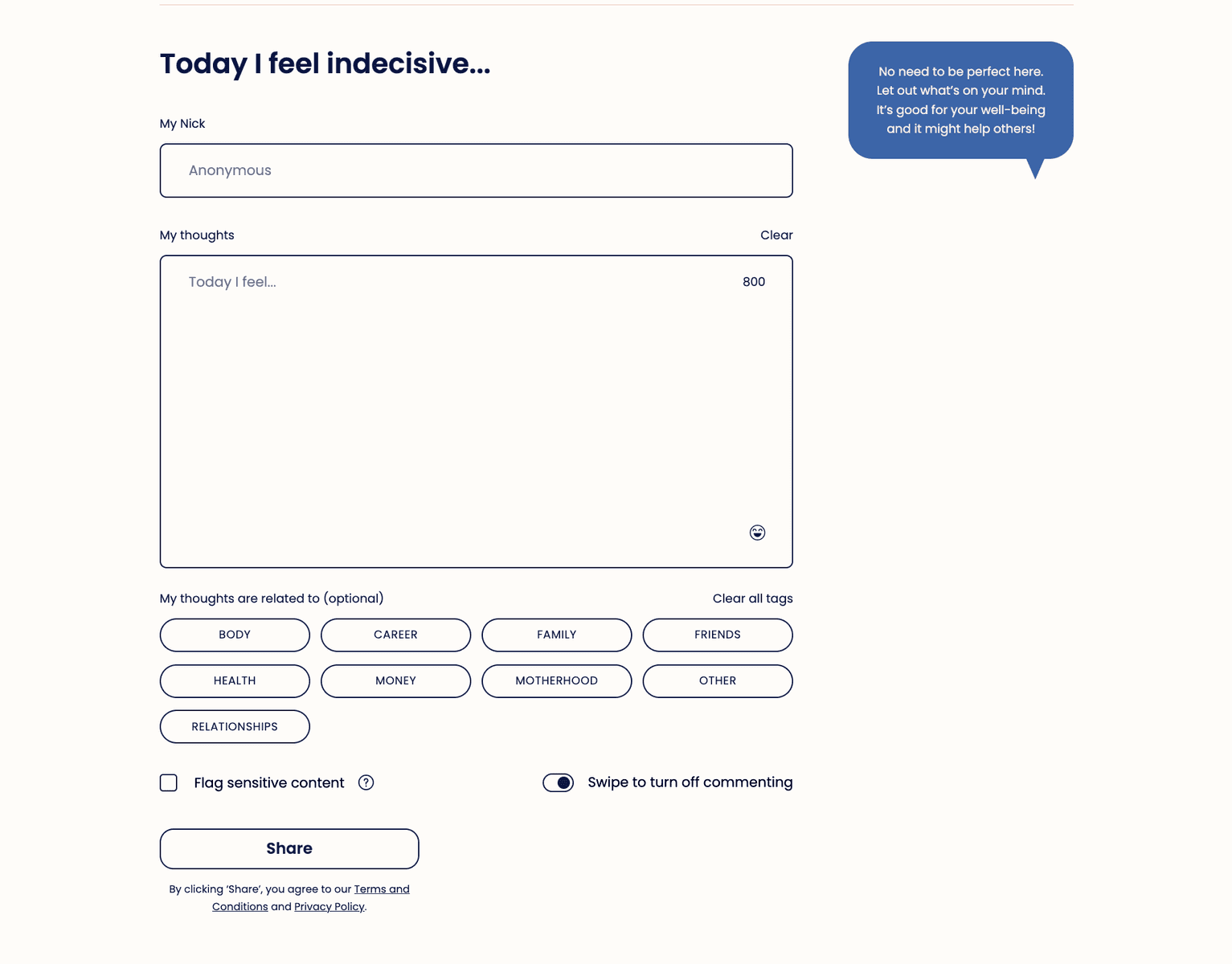
Speaktacular is a platform that's centered around user anonymity. Privacy is at the very core of its design. You don't need to sign up or input any personal information to publish a post.
Why Should I Care About Data Privacy?
Product owners can't be careless in their approach to data. In some cases, it might bring about some serious issues. The reason for that is simple. Keeping users' data safe has become mandated by law. In the European Union, it's the GDPR. It applies to every organization that processes or intends to process the personal data of European citizens in any way, shape, or form. Obviously, GDPR is not the only privacy law you need to comply with. Depending on where your organization is located and whose data is processing, you might have to comply with a wide range of other privacy regulations.

Do Users Care About Data Privacy?
One could argue that internet users don't care about data privacy. It's quite the opposite, though. In 2020, the European Union Agency for Fundamental Rights found that more than a half of Europeans are concerned about criminals or fraudsters accessing their data without their knowledge.
Because of that, you should be transparent about what you do with your users' personal data. Make it as easy as possible for them to delete it. In addition, allow them to choose what data they want to share with you in the first place. Aside from the things that you have to ask them about because of the law, consider extending it to things like personalized recommendations and browsing history.
Implementing such things might take a while, but it's definitely worth it. It will prevent your users from feeling frustrated, manipulated, and even anxious. Instead, they will feel secure and informed. In the long run, it should have a rather positive impact on the reputation of your brand.
Regulatory Compliance and Legal Frameworks
Organizations must understand their legal obligations when it comes to data protection and privacy. This includes complying with regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). These regulations require organizations to implement privacy by design principles, including data minimization, transparency, and accountability. By understanding their legal obligations, organizations can ensure that they are meeting the necessary standards for data protection and privacy.
Navigating the complex landscape of data protection laws can be daunting, but it’s crucial for maintaining legal compliance and avoiding hefty fines. The GDPR, for instance, mandates that organizations must integrate data protection into their processing activities and business practices from the ground up. This means that data minimization, transparency, and accountability aren’t just best practices—they’re legal requirements.
Similarly, the CCPA empowers California residents with greater control over their personal data, requiring businesses to be transparent about data collection and usage. By understanding and adhering to these regulations, organizations not only avoid legal repercussions but also build a foundation of trust with their users. After all, demonstrating a commitment to privacy and data protection can significantly enhance your brand’s reputation and user loyalty.
Benefits of Privacy by Design
One of the key benefits of privacy by design is that it can help to enhance user trust. By prioritizing data protection and privacy, organizations can demonstrate to their users that they are committed to protecting their personal data. This can help to build trust and loyalty with users, which can be beneficial for business. Additionally, privacy by design can help to reduce the risk of data breaches and other privacy-related incidents, which can also help to enhance user trust.
In today’s digital age, users are increasingly aware of privacy risks and are more likely to engage with brands that prioritize their data privacy. By implementing privacy by design principles, organizations can show their users that they take data protection seriously. This proactive approach not only helps in building trust but also fosters long-term loyalty.
Moreover, privacy by design can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and other privacy-invasive events. When users know that their personal data is handled with the utmost care, they are more likely to feel secure and continue using your services. This trust translates into a stronger, more positive relationship with your brand.
In addition to enhancing user trust, privacy by design offers several other benefits:
- Reduced Risk of Data Breaches: By integrating robust data protection measures from the outset, the likelihood of data breaches is minimized.
- Improved Compliance: Adhering to privacy by design principles ensures that your organization meets regulatory requirements, avoiding legal penalties.
- Enhanced Reputation: A commitment to data privacy can significantly boost your brand’s image, making it more attractive to privacy-conscious users.
- Increased Efficiency and Cost Savings: Streamlined data protection processes can lead to operational efficiencies and cost savings in the long run.
- Better Customer Relationships: When users feel their data is safe, they are more likely to engage positively with your brand, leading to improved customer relationships and loyalty.
Overall, privacy by design is an essential strategy for any organization looking to prioritize data protection and privacy. By implementing these principles, you not only comply with legal standards but also build a trustworthy and loyal user base.
So, What Should I Do?
If you don't know where to start when it comes to incorporating privacy by design into the design process, use the GDPR as a point of reference. It outlines six things that we should take into account when designing any product that uses personal data. It's up to the designer to incorporate these principles into the design process and ensure that they are abided by. These foundational principles are essential for guiding your privacy strategies and ensuring compliance with regulations.
Lawfulness, Fairness and Transparency
You should process data in a fair and transparent manner, as well as ensure that everything you do in relation to data processing is legal. Aside from that, it's important that you keep the user in the loop regarding how you process their data and what you do to guarantee its safety.
Purpose Limitation
Don't collect user data just for the sake of collecting user data. Do it with a specific purpose in mind. For instance, if you're collecting user's phone numbers, you might be doing it to provide them with a safe and easy way to recover their account. You shouldn't ask them for their phone number and then store it away simply because you can.
Data Minimization
Before you ask your user for any additional information, ask yourself if you really need it. The amount of data you process should be just enough for you to achieve the purpose for which you collected it in the first place.
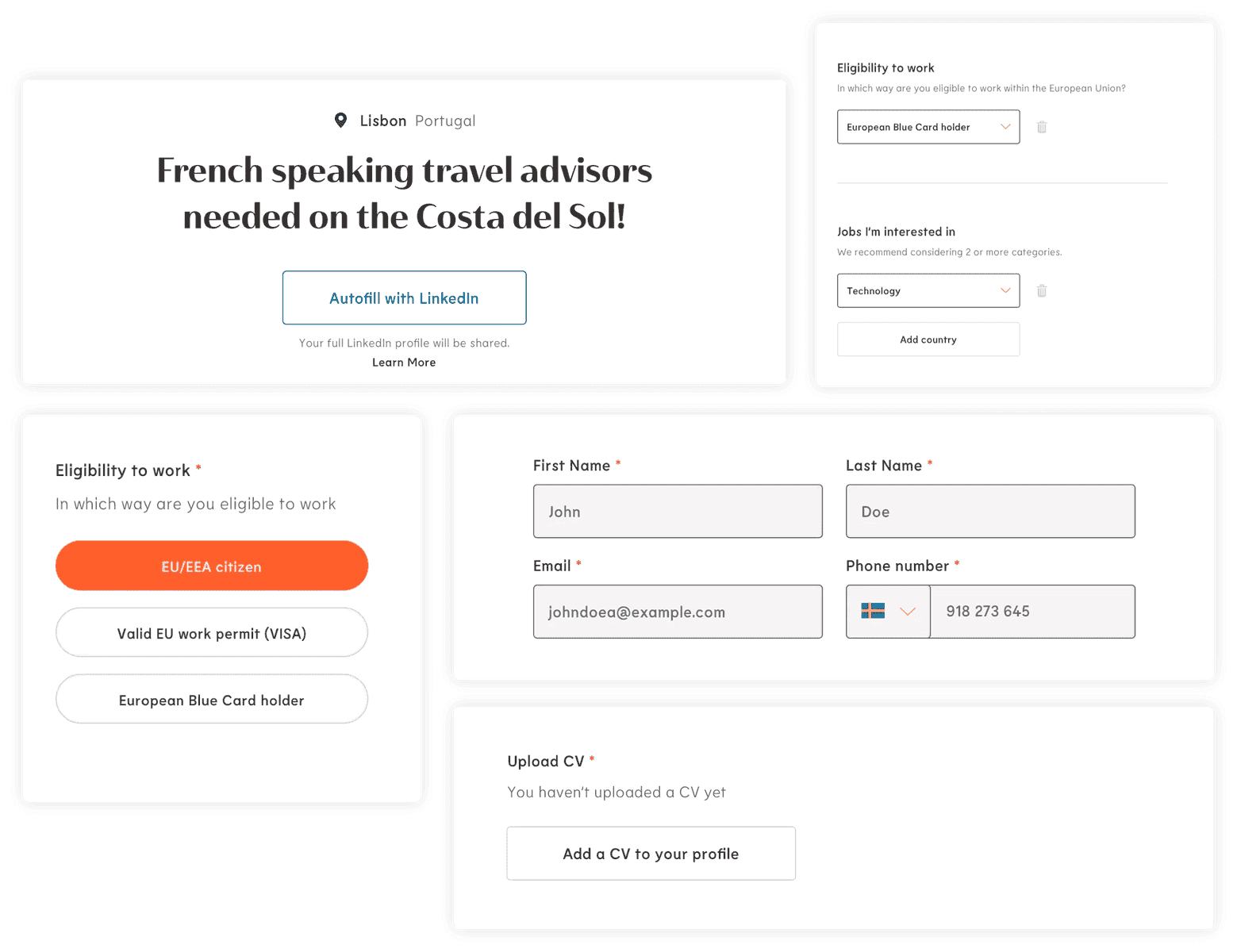
When designing a form, prioritize data minimization. What data do you really need? What do you need it for? It should be communicated from the start so that the user knows what's going on.

Accuracy
The user's data needs to be accurate and up to date. The easiest way to ensure it is to give the user an option to update and delete their information when needed. Ideally, the entire process should be automated. That way, there won't be any bottlenecks when it comes to transporting the data from the user to your systems.
Storage Limitation
When your user uploads their data to your system, you should anonymize it as quickly as possible. That way, if a malicious third-party does get their hands on it, they won't be able to use it against your users.
Integrity and Confidentiality
Last but not least, user data has to be protected against misuse. On top of that, you should do your best to prevent it from being accidentally deleted or corrupted.
Data Privacy Is Worth Paying Attention To
More and more markets perceive data privacy regulations to be an absolute necessity. At the same time, users are becoming increasingly aware of their fundamental right to privacy and the possible consequences of not treating it seriously.
Now, you might want to start incorporating the principles of the privacy by design approach into your day-to-day work. It won't be an easy task, but, as we've already mentioned, it's of utmost importance. It's key to creating a positive brand image and building positive long-term relationships with potential and existing users alike.








